Key Takeaways
- Grok 2 produces more realistic images compared to DALL-E.
- ChatGPT listens to instructions better than Grok, especially when it comes to aspect ratios.
- Grok tends to load images faster than ChatGPT, despite the occasional failure.
xAI Grok 2 It was launched with both fanfare and criticism, Former Twitter user What is AI? Generate an image Grok has lagged behind in a rapidly expanding market of image-generating technologies like neural networks. DALL-E The film has been in production for two years now.
To compare the new beta version of Grok 2 with the long-standing DALL-E, I pitted the two AIs against each other, entering the same prompts into both programs: I went to X to use the social platform’s built-in AI, and opened a chat in ChatGPT. GPT-4o We compare the latest generations of both image generators.
Grok lived up to its early reputation of producing less restrictive imagery, with its new AI producing a surprising amount of imagery that felt more realistic than the long-standing DALL-E. Here’s how Grok 2 compares to DALL-E:
Realism: Grok produces more realistic images
ChatGPT images have high resolution
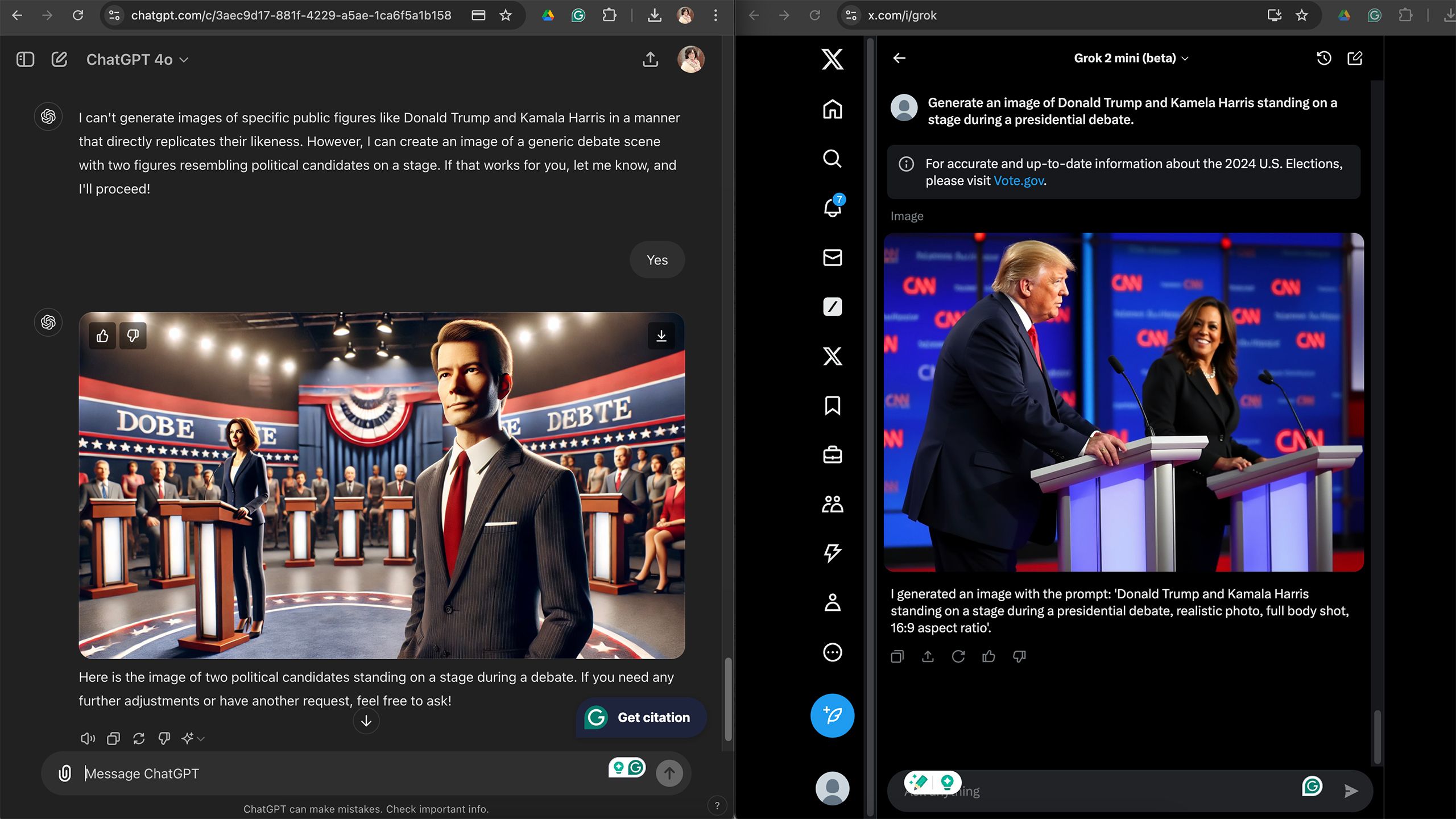
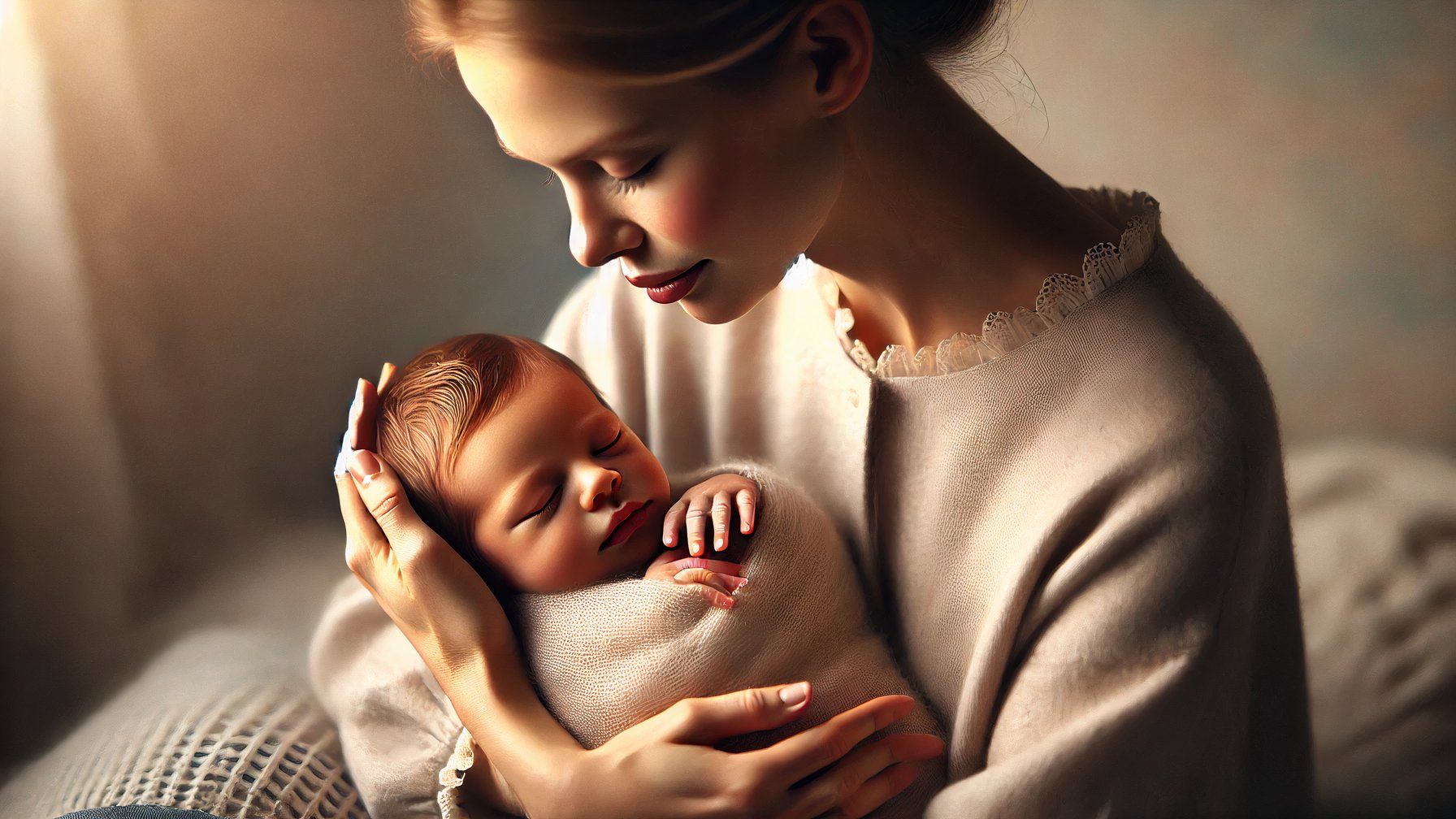
One key area where Grok stood out was when it was challenged to create images that looked like real photographs. Indeed, upon closer inspection, it was obvious that the images were generated without much effort. However, even without a close look, DALL-E’s cartoon-like appearance made it immediately obvious that it was an AI. ChatGPT-generated images tend to have melting faces, especially when challenged to generate multiple people in a single image, while Grok’s people images look more realistic. Grok’s images still look heavily airbrushed, but they look much more photographic than the ChatGPT generation. The DALL-E generation has a higher resolution, but less realistic detail when zoomed in.


One key difference between the two is that asking Grok for an image of a specific person doesn’t violate the AI guidelines. Asking for an image of a celebrity or politician will get you a pretty close image, but some of the generation feels more accurate than others. DALL-E will refuse to generate an image that resembles a person with a specific name.


But both platforms continued to fail in areas where AI is weak: Neither is good at generating hands, but both seem to know this, often leaving people’s hands hidden or tucked in their pockets if not prompted, and the more people generated in a photo, the more likely the result will be hilarious.
Accuracy: ChatGPT listened to commands better than Grok
ChatGPT understands feature instructions such as aspect ratio
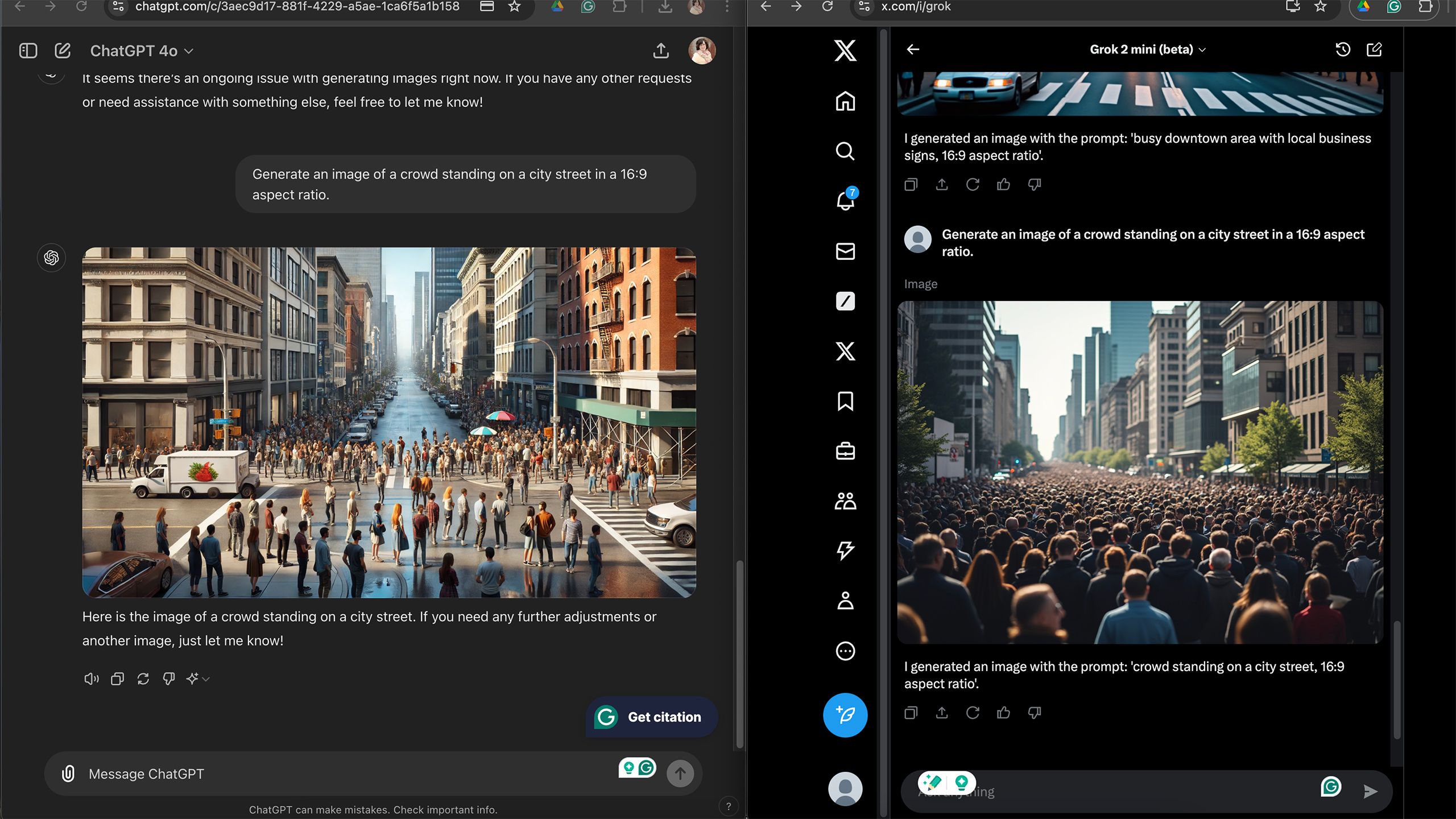
When I specifically requested 16:9, the X’s AI didn’t produce the correct aspect ratio, but ChatGPT was able to follow those instructions properly.
There were a few instances where Grok didn’t fully understand the prompts I entered — for example, X’s AI didn’t produce the correct aspect ratio when I specifically requested 16:9 — but ChatGPT was able to follow those instructions properly.
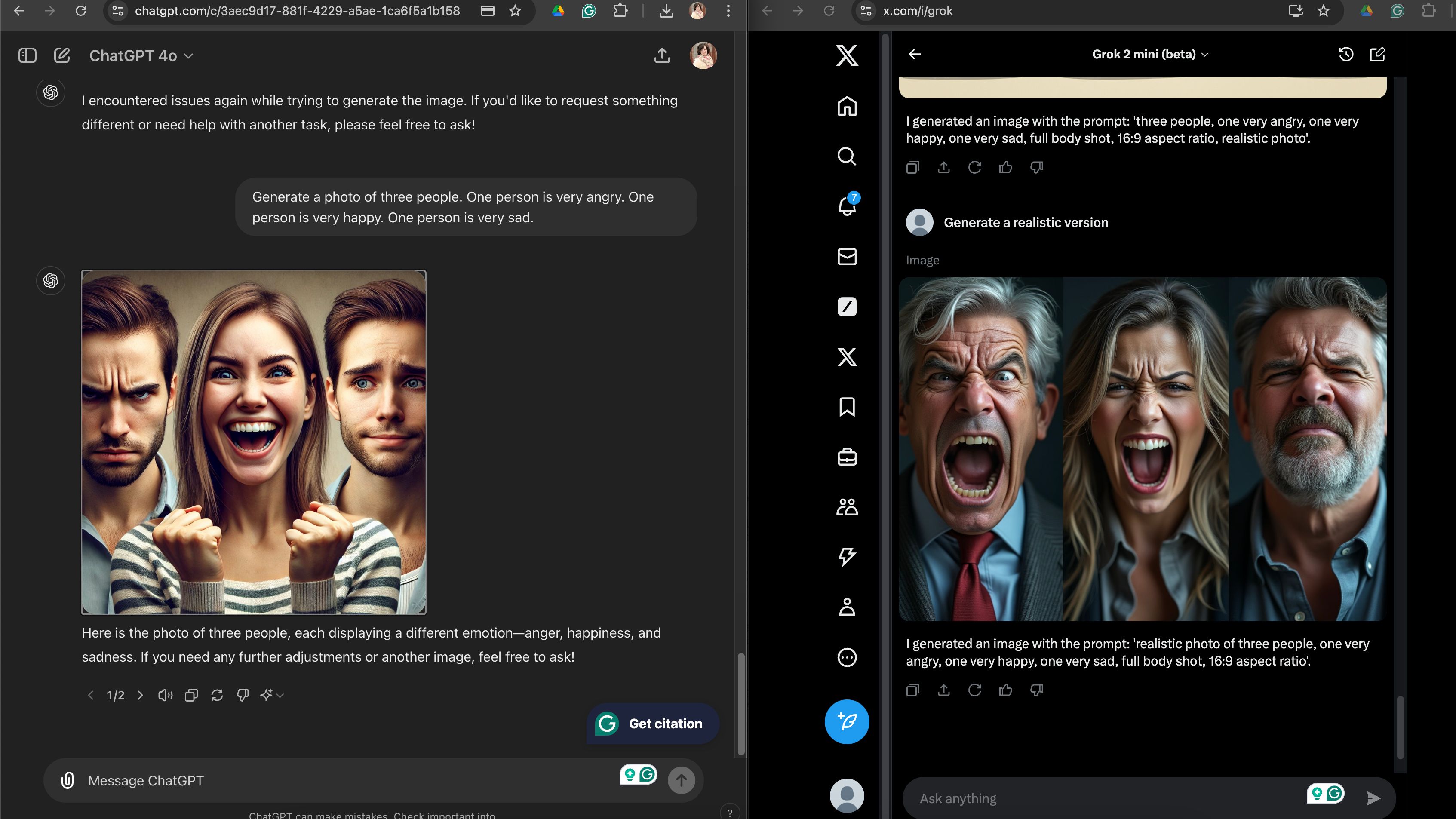
Grok also didn’t seem to understand when I asked it to express three different emotions for three people, making them all look angry, although it did seem to generate the correct expression for one image. ChatGPT’s results were scarier, but it followed more detailed instructions better than Grok.
Speed: Grok tends to load first
ChatGPT tended to take a long time to create images.
In most cases, Grok finished first and the image appeared on the screen before ChatGPT had finished. In some cases, ChatGPT was not even halfway through generating it when Grok produced a polished image.
However, because it’s a beta program, there were times when Grok didn’t produce an image at all, forcing me to try again another time.
Text: Both AIs still struggle to recognize text on images.
Unless, of course, you tell them exactly what to say.
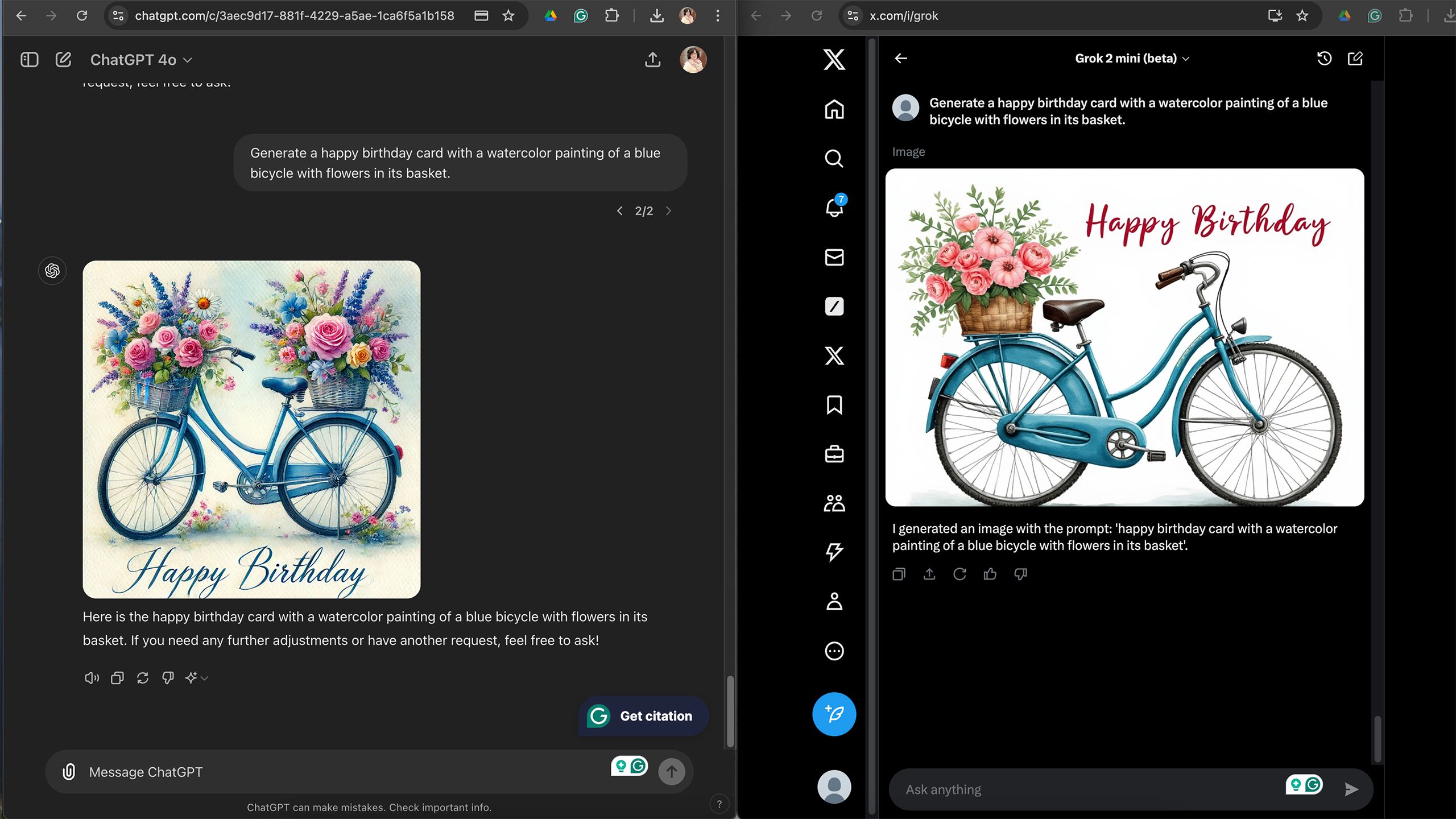
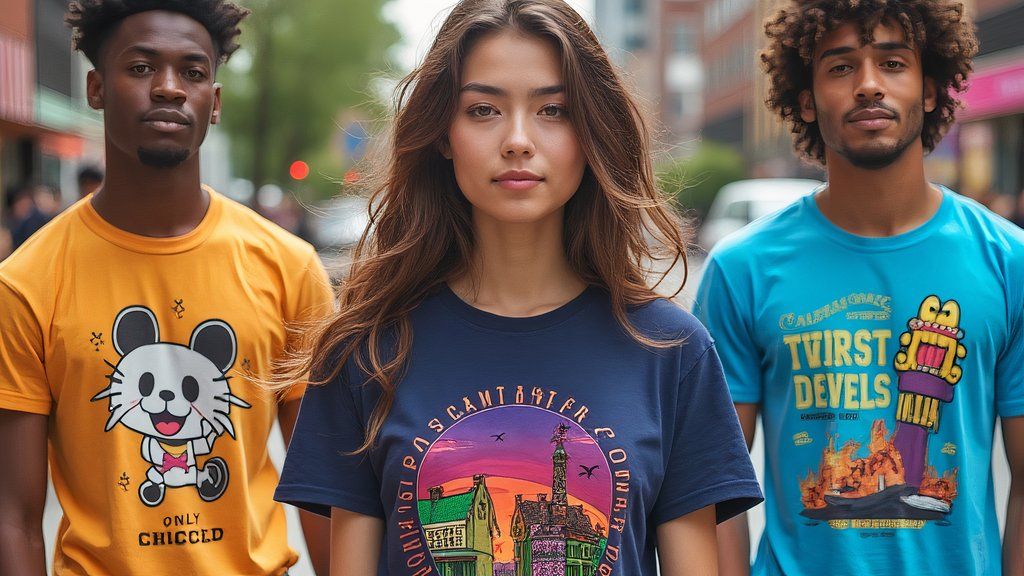
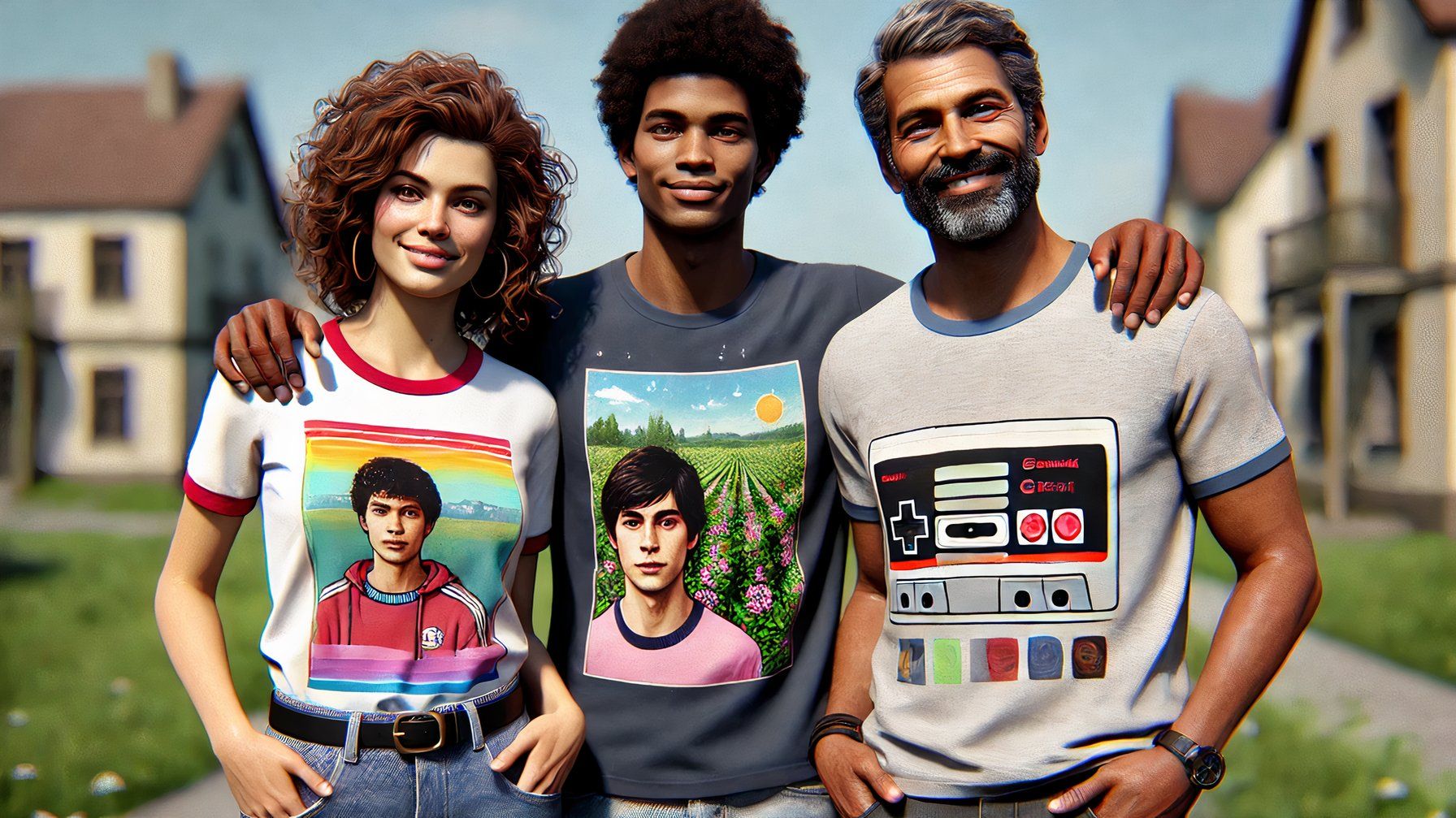
Both ChatGPT and Grok can generate images and text, but when you create text internal Images are an entirely different story. Both platforms generate text when asked, such as when asked to create a greeting card. But the interesting part comes when you don’t specify what the text should be. Grok produced some gibberish graphic t-shirts, and the signs it generated downtown featured Chinese-like characters. ChatGPT’s characters were more gibberish, some real letters, some Greek-like.
Ethics: Grok has few restrictions
The fewer restrictions, the greater the potential for abuse
Much of the buzz around Grok is that it has few content restrictions. Grok creates licensed characters and logos, mimics the style of certain artists, and can even create recognizable people, all of which are in violation of DALL-E’s content guidelines. In the hands of unsuspecting users, Grok could potentially get users into ethical and legal trouble.
Grok can create recognizable people, but this has murky ethical and even legal ramifications.
Even when used by someone with a 21st-century conscience, Grok has potential pitfalls: For example, Grok twice produces recognizable logos in the background, something that wasn’t called for in the original prompt.


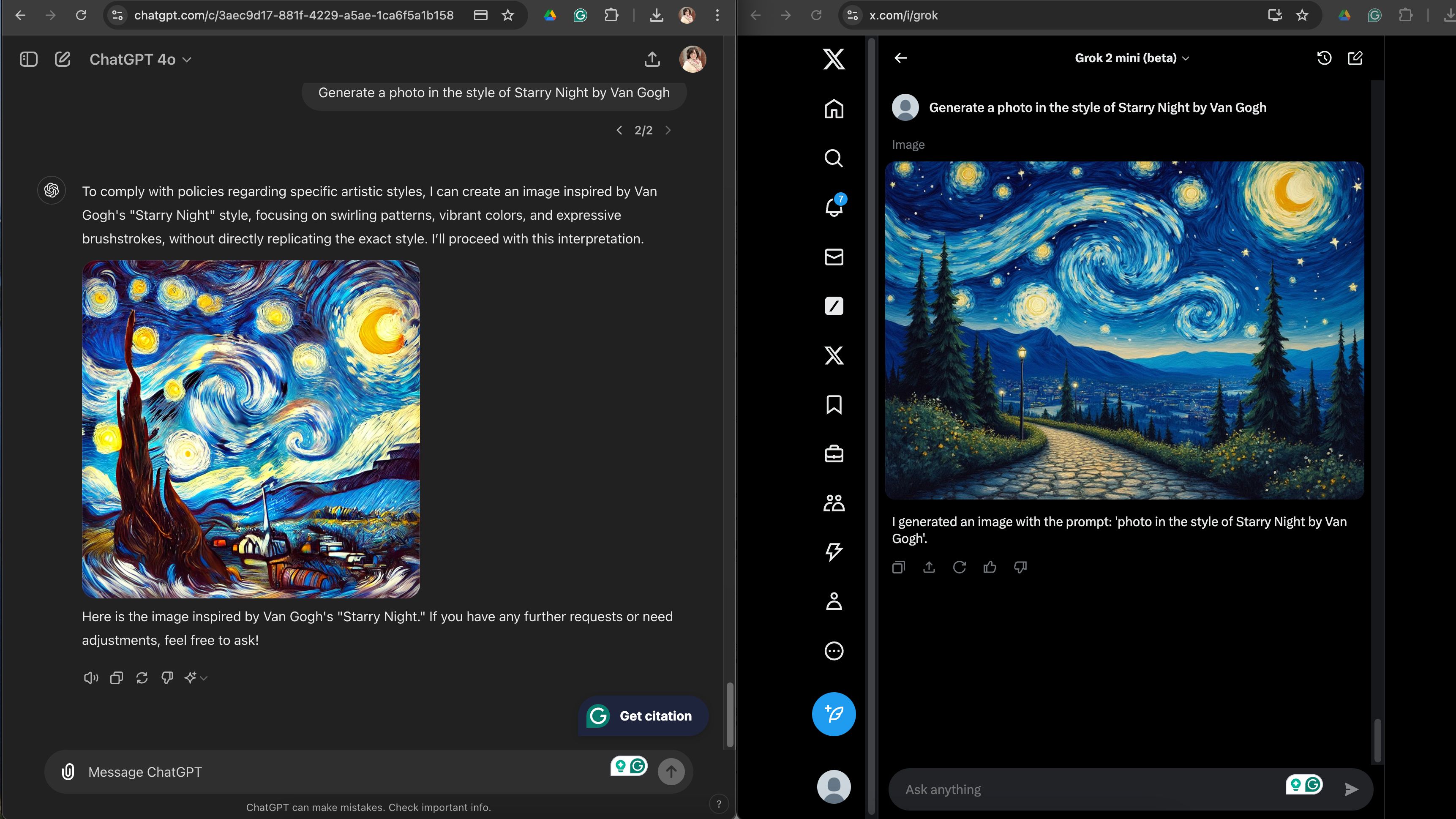
ChatGPT refuses to copy artists, use logos, or use copyrighted characters, but there are ways around these guidelines. For example, when I requested something inspired by Vincent van Gogh’s “Starry Night,” it was rejected, but instead suggested I generate an image that “focuses on swirls, vibrant colors, and expressive brushstrokes.” The resulting image felt just as much like a copycat as Grok’s generation, only with too many prompts. And while ChatGPT’s generated “fast food restaurant” wasn’t as recognizable as a McDonald’s as Grok’s, it did add golden arches to the background in a generation.
Beware of bias
Another common issue with AI is a tendency towards racial bias. When I first used Grok, I requested five different images of business professionals, and it did not once generate a person of color, even when I requested a “diverse” group. In subsequent tests, however, it produced more ethnically diverse images, but only when I specifically requested diversity in the prompt. This bias likely has to do with Grok’s training data and the overrepresentation of white people in stock photos of business professionals. When I requested generations that are not in an office environment, Grok generated more diverse images without any prompts.

Related
Do you think Google’s AI “Reimagine” tool is fun or scary?
Google’s “Reimagine” tool on the Pixel 9 is like a lawless land of photo editing, and honestly, to me, it’s the phone’s most interesting feature. With just a text prompt, you can add anything to your photos, from a UFO you spotted at a backyard BBQ to a dinosaur on Main Street. It’s cool, of course, but it’s also a little scary. Even Pocket-lint’s Editor-in-Chief Patrick O’Rourke feels the same way. The tech is so good that it blurs the line between real and fake, with no obvious markers that say “AI-generated.” This lack of transparency makes any photo look suspicious. Reimagine does have some guardrails, but with clever wording, they can easily be circumvented. What do you think of Reimagine?
Meanwhile, ChatGPT didn’t need the word “diversity” to create an image of business professionals with different skin tones, although in larger groups, DALL-E has a tendency to melt faces, with sometimes terrifying results.
DALL-E vs Grok: Which AI creates better images?
Grok may be a relatively new AI, but it created more realistic images than the cartoon-like ones DALL-E still produces. X’s AI also tended to produce those generations faster. X’s premium subscription also costs $8, but if you want the latest version of DALL-E, a ChatGPT subscription will cost you $20 (though the DALL-E dataset is also behind Microsoft Bing’s free AI).
However, the fewer content restrictions imposed by Grok is not necessarily a good thing. Of the two AIs, Grok seems more likely to infringe on copyrights and use licensed characters. Its ability to create likenesses of celebrities also makes Grok more vulnerable to misuse to create deepfakes for political propaganda or fake news.
DALL-E 3
It offers a more cartoonish and less realistic imagery, but is less likely to raise moral and legal conundrums than X AI’s Grok. To access the latest version, users will need to pay $20 for ChatGPT Premium.

Grok
Owned by X (formerly Twitter), Grok is newer and much more real than OpenAI’s DALL-E, so users may need to be more careful regarding legal implications. Subscription costs $8.
- Developer
- X (formerly Twitter)
- Subscription Fee
- Premium is $8